Scientists have been struggling to warn us for decades that climate change would change dramatically the planet we live on, but at last, they may be getting the attention they deserve thanks to events like Hurricane Irma and Harvey.
They’re the best in their field. I think it’s important to highlight these most famous climate change scientists to keep people aware of the real threat facing the planet.
When climate change is something you can touch, feel and taste, it becomes much more true. If nothing changes, we’ll all be living with a reality where our own homes are becoming less safe as man-made climate change takes its toll on our society.

It’s a crucial time, and the best thing we can do is come together and work towards finding ways of saving our planet and our species. Today, we will talk about the famous scientists who have been instrumental in making us realize the dangers of climate change.
Yeah, so let’s get into it.
The 7 Most Famous Climate Change Scientists
1. Svante Arrhenius
Svante Arrhenius (February 19, 1859–October 2, 1927) is a well-known scientist during his time. The unclassifiable Arrhenius, who spent his entire career working at the intersection of physics and chemistry, was also a man ahead of his time. Some of his works predicted the impact of human activity on climate change, while others supported the hypothesis that life on our planet emerged from extraterrestrials.
Many of his theories, discoveries, and predictions—for which people would later recognize, albeit decades after his death—were very controversial at his time.
2. Michael E. Mann
Michael E. Mann is a climate scientist widely regarded as one of the world’s most influential in the field. He first came to public attention in 1999 as the co-author of the “hockey-stick graph,” which demonstrated the rapid increase in global temperatures since the beginning of the industrial period.
This was the most evident proof anyone had written of the link between human emissions and global warming. This made them a target of Climategate email hacking, personal abuse, and online trolling. In his new book, New Climate War, he claims that the tide is finally moving in a promising direction.
3. Syukuro Manabe
Syukuro “Suki” Manabe (Manabe Shukur, born September 21, 1931) is a Japanese-born American meteorologist and climatologist who pioneered a computer model of global climate change and natural climate changes. He was awarded the 2021 Nobel Prize in Physics with Klaus Hasselmann and Giorgio Parisi for his improvements to the physical modeling of the Earth’s climate, quantifying its variability, and climate change projections.
Manabe subsequently increased the size of this model to two and finally three dimensions. Manabe’s model proved vital in developing a complete, universal, and realistic circulation model of the Earth’s atmosphere.
4. Fred Singer
Fred Singer, born on September 27, 1924, died on April 6, 2020, at 95. Dr. Singer was a physicist specializing in atmospheric and space physics and launched the Science and Environmental Policy Project (SEPP) and the Non-Governmental International Panel on Climate Change (NIPCC).
Fred Singer was one of the “merchants of doubt” named by NCSE board members Naomi Oreskes and Erik M. Conway in their book Merchants of Doubt (2010): a group of scientists who “teamed up with think tanks and private corporations to question scientific data on a variety of contemporary issues,” including tobacco, the Strategic Defense Initiative, acid rain, ozone depletion, as well as climate change.
5. Eunice Newton Foote
Eunice maintained up-to-date on current scientific research, never forgetting her childhood exposure to science. Her 1856 experiment was most likely in reaction to a Scientific American article discussing theories about how the Sun heats the Earth. A discussion ensued as to why mountaintops were colder than valleys. Some thought it was because of the angle of the Sun’s rays, while others said it was because of air density. Foote developed an experiment to settle the argument.
Amid a deluge of floods, heatwaves, and wildfires, the repercussions of human-caused climate change have never been more visible. Eunice Newton Foote discovered in 1856 that the rising carbon dioxide levels in the Earth’s atmosphere would induce warming. She didn’t mean for it to be a warning, but perhaps it should have been in the heart of America’s industrial revolution that humans have a massive impact on the climate”.
Foote’s statements serve as a reminder that the concept of global warming has been around in scientific circles for more than a century.
6. Willi Dansgaard
Willi Dansgaard was a Danish paleoclimatologist (born August 30, 1922 in Copenhagen, Denmark, and died January 8, 201). He was a representative of the Royal Danish Academy of Science and Letters and a Professor of Emeritus of Geophysics at the University of Copenhagen. He was also a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Icelandic Academy of Sciences, and the Danish Geophysical Society, among many other organizations.
Willi Dansgaard was the first to recognize that ice cores excavated from the Antarctic ice sheet may hold information about past climate. The narrative of his career is also the story of how a simple concept in 1952 might become an international sensation in 1969 and then become an entirely new branch of climate and geophysics study.
7. Susan Solomon
Susan Solomon is widely regarded as a pioneer in atmospheric research and has received several awards. One of her most well-known accomplishments is that she was the first to propose and test the hypothesis explaining the cause of Antarctic ozone holes.
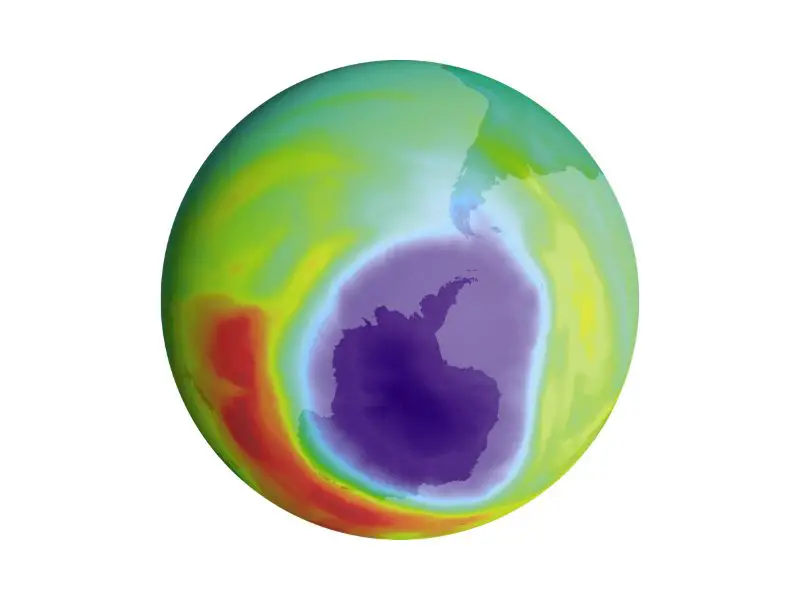
She was also the first to discover the initial chemical measurements showing that man-made chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) were the cause.
Dr. Solomon has also earned several additional awards for her work, including the Asahi Foundation’s Blue Planet Prize, the American Meteorological Society’s Carl-Gustaf Rossby Medal, and the American Geophysical Union’s William Bowie Medal. Solomon Glacier and Solomon Saddle in Antarctica were named in her honor.
Author’s Note
No one knows what our planet’s climate will be like in decades to come, but some researchers and scientists are dedicated to finding out. Names like Susan Solomon, Willi Dansgaard, and Svante Arrhenius might not sound familiar now, but their discoveries will last for generations.
These are just a few of the many names that belong to the top 7 most important climate scientists in history. Some have already proven themselves as global pioneers, and some have earned their stripes in climate science and research.
Let’s all do our part to help mother nature! We can start living a greener and healthier lifestyle by following the advice below.


4 thoughts on “7 Famous Climate Change Scientists: Experts Who Have Shed Light on Climate Change”