Pollution in Spain is a growing concern for both citizens and the government. Rising levels of air pollution, water contamination, and waste management create an unsustainable situation that threatens public health and the environment.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes of pollution in Spain, the current state of air quality, and what steps can be taken to address them.
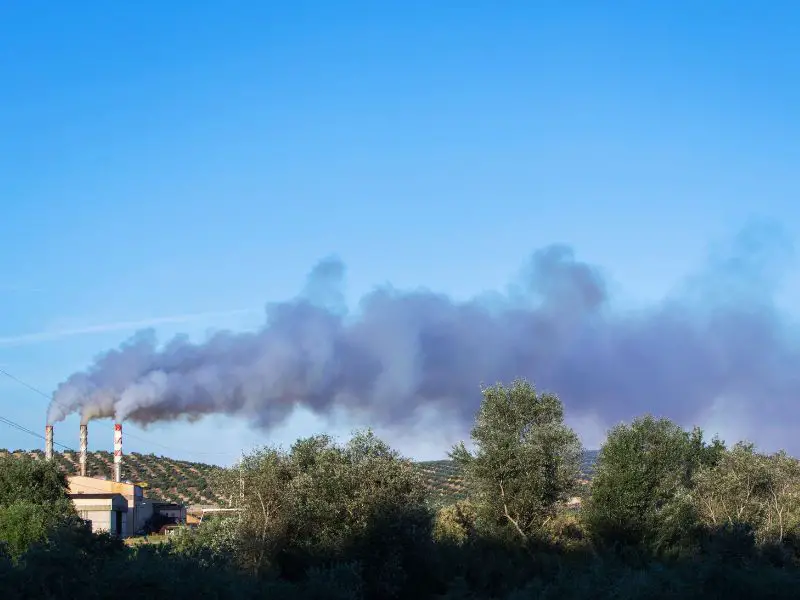

Overview of Pollution in Spain
At the beginning of 2021, Spain was enjoying a period of “Good” quality air with a US AQI reading of 40, placing it in the World Ranking of dirty cities at number 82 out of a possible 98. However, according to a report by T&E’s Spanish member Ecologistas en Acción, 97% of Spain’s population is exposed to harmful air pollution from particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and ground-level ozone.
In 2015, Spain was labeled Europe’s most polluted country by the European Environment Agency (EEA). This alarming statistic highlights the magnitude of environmental pollution in Spain and its impact on the environment and health.
Here are various types of pollution in Spain and what measures are being put in place to address them.
Pollution in Spain
1. Air Pollution in Spain
Unfortunately, air pollution continues to be a significant problem in Spain. Car emissions are one of the leading causes of air pollution in Spanish cities, with about 15 million Spaniards being exposed to harmful levels of air pollution.
“Every breath is a giveaway dance between you and the trees.”
– Amit Ray
In 2019, Spain announced its commitment to reducing short-lived climate pollutants and has taken steps to tackle health, climate change, and air pollution.
2. Water Pollution in Spain
Water pollution is a significant issue in Spain. In some of Spain’s central pig farming regions, groundwater nitrate levels are four times higher than the legal threshold. This has a detrimental effect on water quality and can make drinking water unsafe. It can also increase the levels of toxic pollutants in soil and water, which can further damage the environment and cause long-term health issues.
3. Soil Pollution in Spain
In addition to air, water, and light pollution, Spain also faces severe soil pollution. The primary sources of soil pollution are industrial processes, agricultural activities, and the improper disposal of hazardous waste. Agricultural runoff is a significant cause of water pollution in Spain, as it can lead to heightened levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in the soil. This can lead to a decrease in soil fertility and an increase in soil erosion.
Industrial processes can also release toxic substances into the soil, contaminating crops and water sources. Furthermore, the improper disposal of hazardous waste can lead to soil contamination with dangerous chemicals. All these forms of soil pollution in Spain harm the environment and human health.

“Soil is not a lifeless, inert substance. It is teeming with life and plays a vital role in sustaining all life on Earth.”
– Rachel Carson
4. Light Pollution in Spain
Lighting pollution is a growing concern in Spain due to the increased use of artificial lighting. This is particularly evident in large cities such as Madrid and Barcelona, where light pollution is estimated to be up to four times higher than the legal threshold. Light pollution affects both human health and the environment, as it negatively affects the sleeping patterns of humans and animals and can interfere with natural cycles such as photosynthesis.
To reduce light pollution, Spain has implemented several energy efficiency measures, such as the introduction of LED lighting and the enforcement of regulations limiting the use of artificial lighting in certain areas.
5. Noise Pollution in Spain
Noise pollution is caused by various sources, ranging from traffic, construction, and industry to recreational activities. According to the World Health Organization, noise levels above 55 decibels can cause hearing impairment, sleep disturbance, and cardiovascular and cognitive problems. Spain has taken steps to reduce noise pollution by implementing legislation and regulations to limit the noise produced by transportation and industry and by introducing more efficient urban planning practices. However, more effort needs to be done to reduce the impact of noise pollution on the environment and health of Spanish citizens.
6. Chemical Pollution in Spain
In addition to air, water, and soil pollution, Spain is also facing an issue with chemical pollution. Industrial sites, agricultural activities, and other activities have led to increased contamination of the environment with hazardous chemicals. These chemicals can severely impact human health, potentially causing respiratory problems, reproductive issues, and even cancer.
In some of Spain’s central pig farming regions, groundwater nitrate levels are four times higher than the legal threshold of nitrate levels set by the EU. This highlights the need for better regulations and enforcement regarding controlling chemical pollution in Spain.
7. Marine Pollution in Spain
Although air pollution is Spain’s most severe form of pollution, marine pollution is also a problem. Spain is one of the European countries that releases the most pollutant substances into the sea. This is due to various sources, including industrial and agricultural activities, urban wastewater discharges, and illegal dumping. These pollutants can cause severe damage to marine ecosystems, affecting marine life and putting the health of people who rely on the sea for their livelihoods at risk.
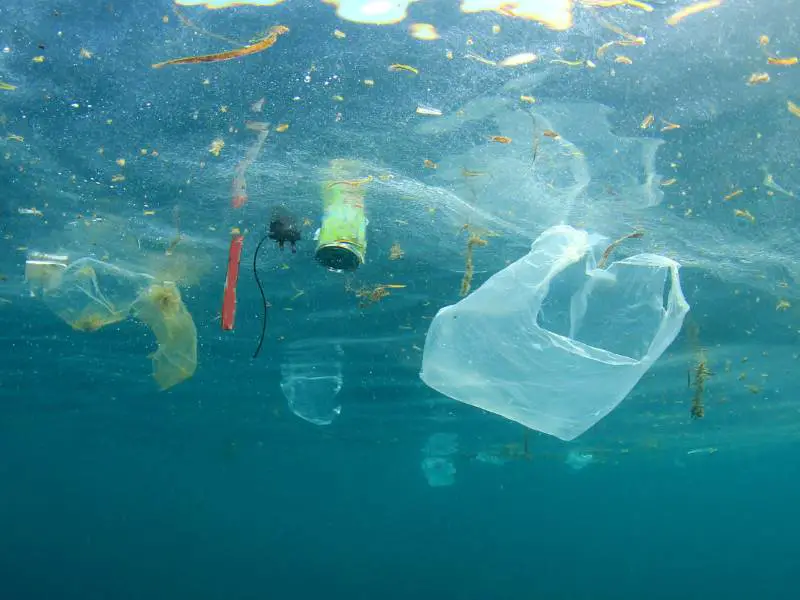

The Impact of Pollution on the Environment and Health
The impact of pollution on the environment and health in Spain is very concerning. Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) air pollution levels in Madrid and Barcelona were found to exceed EU limits between 2010 and 2018. Furthermore, groundwater nitrate levels in some of Spain’s central pig farming regions were found to be up to four times higher than the legal threshold. All of these factors directly affect Spanish citizens’ health and the environment in which they live.
Solutions to Pollution in Spain
As pollution is a significant concern in Spain, it is important to consider solutions to address it. Several measures can be taken to reduce the amount of pollution in Spain. For instance, it is essential to invest in cleaner sources of energy, such as renewable energies like wind and solar.
“The environment is where we all meet; where we all have a mutual interest; it is the one thing all of us share.”
— Lady Bird Johnson
Furthermore, the implementation of stricter regulations on emissions and improved waste management policies would help significantly reduce air, water, and soil pollution. In addition, citizens must be educated on the importance of reducing their environmental footprint by reducing energy consumption and avoiding single-use plastics.
Finally, enforcing laws that protect the environment and punish those who break them is also essential. If implemented correctly and consistently, these measures could help scale down the number of pollutants released into the atmosphere and improve public health in Spain.
Related: Ocean Pollution, Effective Pollution Prevention Strategies, Plastic Pollution
Bottomline
There is an urgent need to address European air and water quality. Air and waterborne diseases have been rising in recent years due to population growth and the increased use of natural resources.
Meanwhile, water and air pollution also affect the environment adversely. To address this issue effectively and reduce the impact of air and water quality on human health and the environment in Europe, governments must enforce tighter environmental regulations and take other steps to improve air quality and protect water resources. As citizens, we can also help by contributing to these initiatives and reducing our environmental footprint through recycling and eco-friendly products.

