E-cars are becoming increasingly prevalent worldwide because of their environmental friendliness and low maintenance costs. However, a new survey has found that many people are hard to convince of the benefits of green cars.
A recent survey has found that while many people are driving electric vehicles (EVs), they remain unsure of their benefits for the environment or their finances. This article will examine the pros and cons of owning an e-car, its history, and common myths and facts about e-cars.

History of Electric Cars
Electronic vehicles have captured people’s attention throughout the decade. While electric cars have been around since 1832, electric vehicle technology has drastically improved over recent years.
The search for an energy-efficient vehicle impressed many people and led to the development of electric cars. The first electronically powered cars appeared in the late 20th century.
Invented by William Morrison of Des Moines, Iowa, in 1890 – 91, the first electric car was unsuccessful mainly due to its low energy efficiency (efficiency was only about 6%). It was not until the 20th century that electric cars became popular. In 1997, the Prius became one of the first mass-marketed hybrid/electric cars in the world.
In 1999, Honda produced the first commercially successful electric car, the EV Plus). And in 2008, Tesla released its first electric sports car, the Tesla Roadster, beginning the modern era of Electric Vehicles.
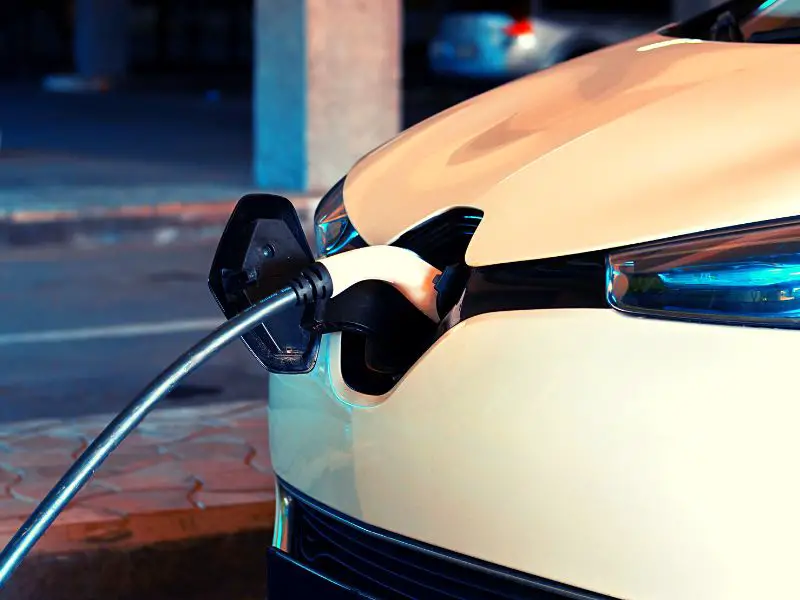
How To Charge an Electric Car?
You can charge electric cars by plugging them into a regular household outlet like other household appliances. And unlike fossil fuels-powered cars, electric vehicles have far fewer moving parts, requiring much less maintenance. Electric cars have zero emissions, so they’re better for the environment.
Of course, electric cars are much quieter than internal combustion cars, so they’re better for urban and suburban neighborhoods. Because of their less maintenance and operating costs (at least compared to gasoline-powered cars), in an estimate, electric vehicles could be more cost-competitive than gas-powered cars.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Vehicles?
Electric vehicles have several advantages over standard cars. The electricity that powers the cars can ideally be from natural sources that will never run out, such as wind, solar, hydroelectric dams, and nuclear generators. Since these power sources will never run out, they eliminate one of the significant concerns of fossil fuels.
Advantages
- They are more eco-friendly because they do not produce any exhaust fumes. They are quieter than fossil fuel-powered vehicles (because they don’t make any engine noises);
- They do not use gasoline, which means they will be cheaper to maintain in the future, mainly because gasoline is a finite resource, and its price is expected to increase;
- It is predicted that the cost of electricity will decrease over the next few years, making the vehicles even cheaper to operate;
- Electric vehicles can be powered at home with a regular electrical outlet;
- Because they have no internal combustion engine, electric cars require less maintenance than similar gasoline-powered vehicles. As a result, operating costs are lower than in fossil fuel-powered cars. However, they require periodic maintenance of the battery packs (for example, replacing malfunctioning battery cells and rebalancing the battery pack when cells are removed or added).
Disadvantages
- Environmental problems: EVs produce less pollution and waste than conventional gasoline-powered cars. However, the electricity they use, may come from both traditional power plants that burn fossil fuels and from renewable sources that may produce some pollution and waste themselves. As a result, the overall impact of EVs on pollution and waste depends on the source of electric power and on the efficiency of the power plants that supply the power.
- Insufficient battery capacity: EV batteries typically provide less driving range than gasoline-powered cars with the same weight due to lower specific energy for a given weight. This limitation is lessening as battery technology improves and electric vehicles become lighter by eliminating nonessential elements.
- Cost: Electric vehicles are more expensive than gasoline-powered cars. The additional fee is due primarily to the battery and charging equipment. They can be more expensive than similar conventional cars only when the total cost of ownership is considered over the vehicle’s lifetime. Electric cars are expected to cost less to operate than comparable conventional vehicles because of lower fuel and maintenance costs. Still, the cost of electricity has to be taken into consideration.
Are Electric Car Batteries Greener?
Vehicles’ emissions measure the levels of toxic chemicals emitted into the atmosphere. The environmental effects of these emissions can lead to acid rain and cause adverse effects on human health and the environment. The pollution from the fumes also increases global warming and the greenhouse effect, which drives climate change. To reduce the environmental impact of vehicles, emissions must be as little as possible.
This is where an electric car can help. Electric vehicles emit zero toxic gasses, which helps reduce climate change’s impact by significantly reducing overall air pollution. At the same time, an electric car’s battery is recyclable and reduces the need for mining for metals, which can also reduce the environmental impacts of vehicle manufacturing.
How Many Electric Cars Are on the Road?
Following a decade of sustained expansion, there are currently more than 10 million electric vehicles on the road; this number accounts for less than one percent of the total automotive worldwide.
The Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario forecasts that there will be 300 million electric cars on the road in 2030 and that these vehicles will account for over 60 percent of new car sales. This is a significant expansion from the 4.6 percent of new cars sold in 2020.
Which Countries Drive the Most Electric Cars?
Norway has the highest number of citizens using electric cars, with 1 in 10 vehicles being electric or hybrid. 95% of Norwegians have access to a charging station. In 2017, Norway had over 25% of all-electric cars sold in Europe. This is thanks to the government for implementing green policies and encouraging the use of electric vehicles in their country. Norway has one of the world’s highest levels of electric cars per capita.
The European country was the first to introduce a tax break for buying an electric car in 1994. This tax break was revoked in 2017, but Norway still offers incentives to encourage people to purchase environmentally-friendly vehicles. For example, those who buy an electric car will receive a tax break for off-street parking and toll fees, and electric car drivers are exempt from toll fees on highways and bridges throughout the country. Norway also implemented a free charging system nationwide, offering free charging stations at restaurants, shops, and other public places.
Myths and Facts About Electric Cars
Contrary to what some may assume, here’s a quick look at ten common myths and facts about electric cars that you should know.
1. Electric Cars Are More Expensive to Purchase Than Conventional Cars
This is not true, as the total cost of ownership for an electric car is one-third less than that of a conventional vehicle. The initial cost of purchasing an electric is indeed higher than that of a classic car; however, driving a car that costs less to run will give you more value for your money over time.
2. Electric Cars Can Never Be as Fast as Conventional Cars
This isn’t true either, as electric cars are faster than conventional cars when running on a well-maintained road. This is also true regarding speed charging, as electric vehicles can reach 80% battery capacity in as little as 20 minutes when charged at a fast-charging station.
3. Electric Cars Can’t Be Driven Long Distances Without Recharging
This isn’t true, as electric cars range about 200-350 miles (320 – 500 km) under ideal conditions and when driven at low speeds. This is more than sufficient for most drivers’ daily driving needs.
4. Electric Cars Are Expensive to Maintain
This certainly isn’t true, as electric cars require little maintenance. Electric cars only have four moving parts, which are easy to repair and fix when something goes wrong. Electric cars have a longer lifespan than traditional vehicles as they don’t need as many repairs or replacements.
5. Electric Cars Take a Long Time to Charge
One of the biggest misinterpretations about electric cars is that it takes between 45 minutes and 12 hours to fully charge an electric vehicle. However, most charging stations have various charging options, including fast chargers, which can fully charge an electric car in as little as 25 minutes.
6. Electric Cars Are Only Good in Big Cities
This is false, as electric cars are just as practical to drive on country roads as in big cities. An electric car’s battery provides more power on country roads, and the vehicle’s regenerative braking system boosts the car’s range and fuel economy.
7. Electric Cars Are More Costly Than Their Gasoline Counterparts Over Five Years
According to a recent study and research conducted by the University of Michigan, the upfront cost of an electric car is more than $11,000 more on average compared to a gasoline-powered vehicle. However, when you consider the reduced operating and maintenance costs of an electric car compared to a gasoline-powered vehicle, the total cost of ownership over five years is approximately $8,500 more on average than a comparable gasoline-powered vehicle.
8. Electric Cars Have Less Range Than Gas-Powered Vehicles
The average electric range of today’s electric cars is 250 to 300 miles compared to the average gasoline-powered vehicle, which may have a range of 400 to 500 miles or more. However, as battery technology improves and charging stations become more available throughout the U.S. and worldwide, the driving range of electric cars is expected to increase significantly over the next few years.

Author’s Note
Electric vehicles are more environmentally friendly and cheaper to operate and maintain. It will take time for electric cars to reach parity with fossil fuel-powered vehicles in terms of costs. Still, we hope they’re widely adopted soon so we can achieve significant reductions on our emissions on a global scale.


5 thoughts on “Electric Cars: How Environmentally Friendly and Easy to Maintain Are They?”